What's the difference between carbon steel profiles and stainless steel profiles?
What's the difference between carbon steel profiles and stainless steel profiles?
Profiles made from coated strips, Sendzimir galvanizing, Aluzinc, Zincomagnesium and profiles made from stainless steel strips: characteristics and differences
Each type of metal has a specific composition and characteristics, such as corrosion resistance, which make it more or less suitable for particular uses. Knowing the difference between carbon steel profiles and stainless steel profiles is essential to choose the type of profile that best suits your needs. Let us discover together the main characteristics of these two materials.
The so-called galvanized steel is obtained by immersion, or subsequent treatment of carbon steel (chemical analysis predominantly iron-carbon) in order to maintain the mechanical characteristics controlled for parameters of strength, hardness and elongation.
The zinc coated can be distinguished according to the use, intended application and resistance to external agents such as atmospheric agents, acidic or basic environments or further protective coating or plasticizing treatments.
Galvanised steel
Electrogalvanised steels (EN 10152:2017 - EN 10268:2006), cold-coated by static electrolysis, are generally used for applications with low thicknesses and/or in favourable climatic conditions for a more refined aesthetic appearance or for subsequent further protective surface treatments, such as painting or enamelling. For this reason they are often used in the automotive sector and in the construction of household appliances and interior furnishings.
Hot-dip galvanised steel
Hot-dip galvanised steels (EN 10346:2015 - EN 10346:2015 - EN 10346:2015), produced by hot-dip galvanisation (a process called "galvanisation"), are able to ensure greater corrosion resistance thanks to a greater thickness and the different types of coating used.
The galvanizing process is characterized by the continuous dragging of the strip in a bath of molten zinc. The drag rate will determine the thickness of the zinc layer to be formed. Some examples of coatings:
- Galvanized Sendzimir (Zn >99%)
- Galfan zinc-aluminium alloy (Zn 95%-Al 5%)
- Aluzinc alloy aluminium-zinc-silicon (55%-Zn 43.4%- Si 1.6%)
- Aluminium-silicon alloy (90% to 10%)
- Zinc - Magnesium alloy aluminum-magnesium (Mg+Al 1.5-8% - Mg>0.2%).
Stainless steel (inox)
Stainless steel (UNI EN 10029:2011) is characterized by the almost total absence of carbon (C <0.07%) content Chromium (Cr > 10.5%). The latter favours the natural passivation layer, giving this type of steel a high resistance to atmospheric corrosion (higher than galvanized steel), in addition to increased resistance to heat and corrosion caused by the use of acids or corrosive products. Thanks to its brilliant appearance and the molecular compact chemical and physical formula, it is widely used in the agro-food and pharmaceutical sectors.
Unlike coated steels, stainless steel is more expensive because of the high production costs but guarantees an almost eternal service life, is more hygienic and cleaner and does not fear the wear of time even if scratched or engraved thanks to the action of chromium that reacts chemically inside. The durability of coated steels, on the other hand, depends both on weather and mechanical wear.
Galvanized steel and stainless steel: the differences
The main differences between galvanized steel profiles and stainless steel profiles can be identified in two main aspects:
- cost: stainless steel is much more expensive because the process of construction is more complex; galvanized steel, on the other hand, is cheaper because galvanization is a simple and fast process;
- durability: stainless steel lasts longer and, if scratched, continues to be protected because zinc is also found inside. Galvanized steel will be protected only as long as zinc is present on the surface.
The difference between these two materials also depends on the type of use and the different situations. To cite an example, we think of photovoltaic panels, which are not subject to scratches but only to atmospheric agents: in this case galvanized steel is preferred as cheaper.
To understand how long the zinc coating will last on these plants, you can refer to the technical data related to the annual loss of zinc according to the environment in which the product will be exposed. This will help define the type of galvanization required.
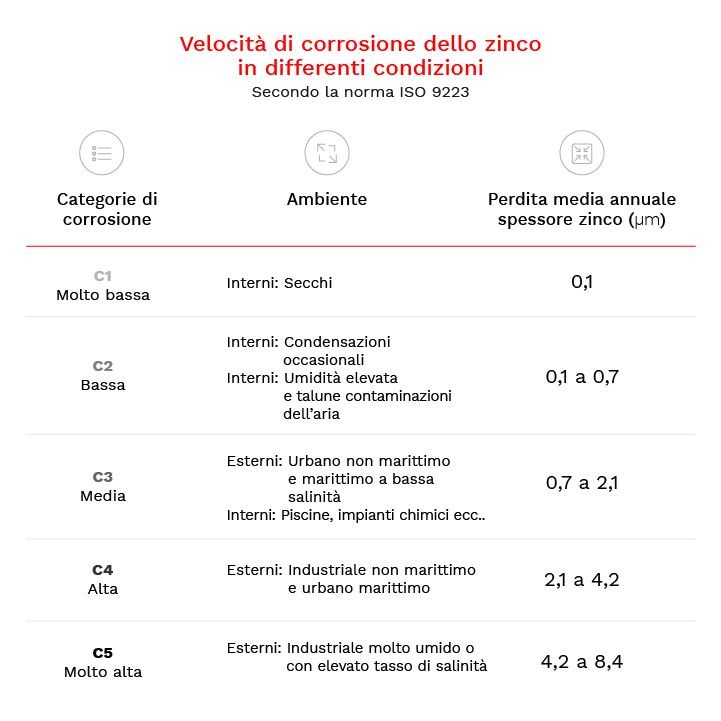

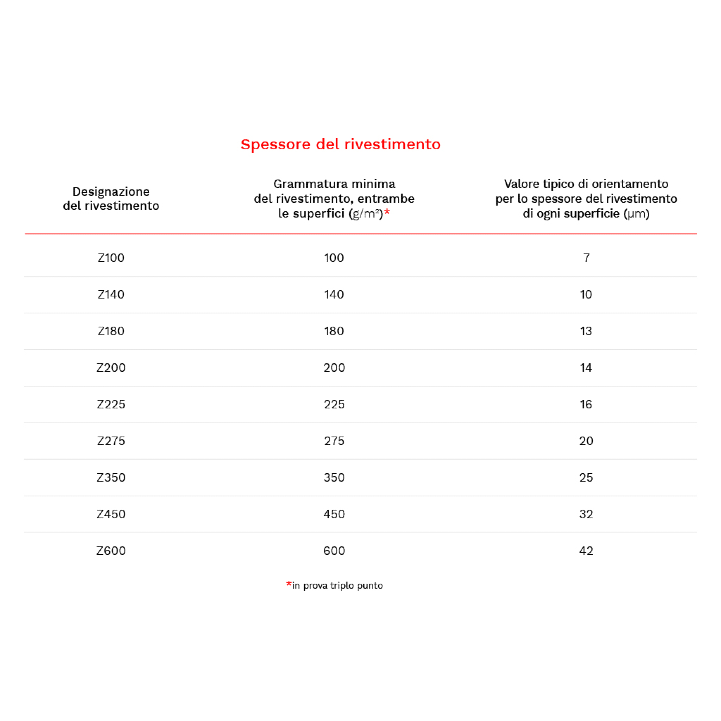
Taking into account a "normal" environment (non-maritime or low-salinity marine urban exterior) with a loss of about 1 micron per year we could identify as optimal solution a coating Z275, The average life of a photovoltaic panel is around 20 years.
For more information on carbon steel profiles, stainless steel profiles or other types of profiles and services offered by Profilsystem, contact us!